B as bulging
Bulging in 3D printing: Understand and correct
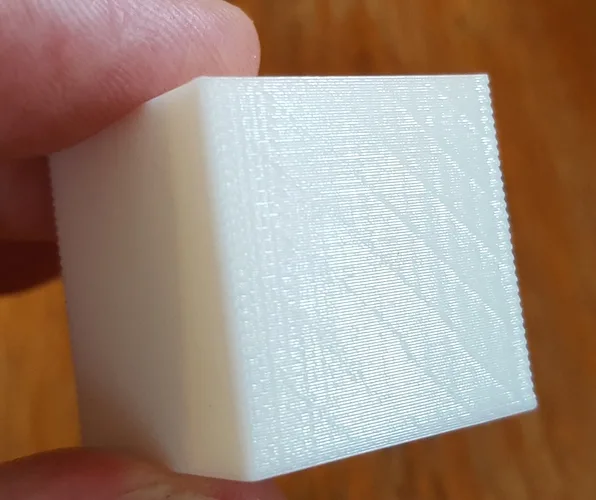
“Bulging” is a common defect in 3D printing, manifesting itself by bumps or unwanted swelling on the surface of the object.
It can affect the aesthetics and solidity of the room.

Causes of bulging:
Too high printing temperature: the filament melts too quickly and deforms.
Insufficient cooling: the filament does not have time to solidify before the next layer.
Incorrect printing settings: poor print speed, retraction, adhesion between diapers.
3D model problems: complex geometry, too fine walls, poorly designed supports.
Solutions to avoid bulging:
Adjusting the printing temperature: lowering it by a few degrees can make a big difference.
Reduce printing speed: some filaments do not like high speed.
Improve cooling: increase ventilation, print in a cooler room.
Optimizing printing parameters: reducing printing speed, increasing retraction, adjusting adhesion between diapers, changing the generation of Arachne wall instead of classic.
Modify the 3D model: simplify the geometry, thicken the walls, lead the supports.
Use a better quality filament: some filaments are more resistant to warping and bulging.
Additional advice:
Properly calibrate your filament.
Test different printing configurations to find the best solution for your model.
In conclusion, Bulging is a frequent problem in 3D printing, but it can be easily avoided by understanding the causes and applying adequate solutions.
